Traveling at 430 km/h in the World's Fastest Transportation
- STEM To Go

- Jul 29, 2020
- 3 min read
Is it possible to travel at a speed of 430 km/h? If there's a way, surely it isn't safe, but only a mere concept of what's to come in the future. However, when there's a will, there's a way. Introducing inventive technology that that is changing the field of engineering and technology is the Maglev Train, or fully, the magnetic levitation train. Maglev trains are the new 21st century modern transportation, and it's already been in practice for a while. Results show that maglev trains are actually the safest and comfortable rapid transport system in the world, with some major players like Japan and China! Read more to understand how maglev trains use magnetic force as a way to convey momentum, and how it is slowly going to be implemented in many countries worldwide for its properties of safety and effectiveness.

How Do They Work?
Maglev trains are the new revolutionary land transportation of the 21st century. Maglev trains are not designed with wheels or rails. Instead, they have guideways, which the maglev trains float above it, making it an energy-efficient transit choice. Electromagnetic suspension depends on the attractive force. It is operated by either EMS- attraction and EMS- repulsion. EMS repulsion uses the repulsive force of efficient, conducive magnets attached on the guideways, as well as attached on the maglev train to perform levitation and move the train at a faster speed. Once the maglev train begins to move, the magnets on the train and the magnets on the guideways slide past each other to generate repulsive force. Electromagnets on the vehicle are drawn toward a pair of steel rails. The vehicle floats above the steel rails, but the magnets wrap beneath the rail. It uses attractive force between magnets present on the train’s sides and on the guideway to levitate the train and pulls the train forward.
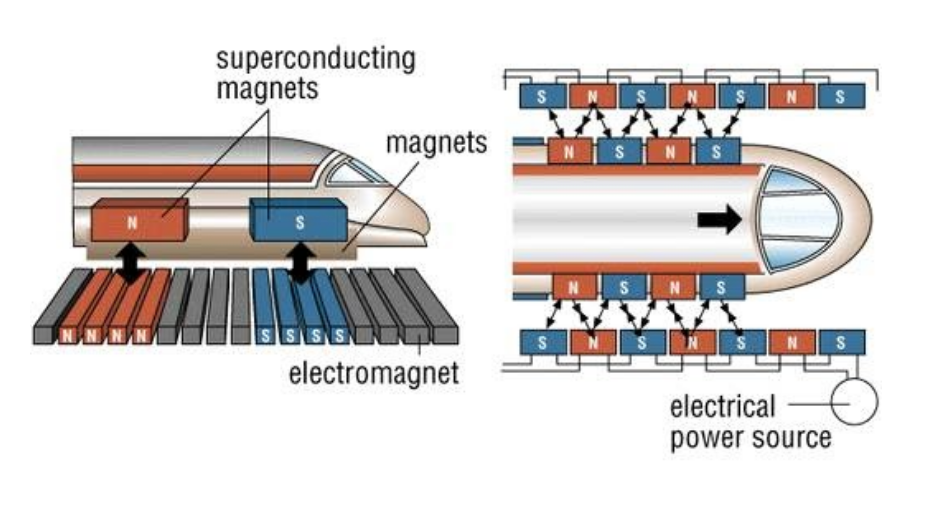
The main priority a maglev system must achieve is to able to stay suspended off the ground using electromagnetic levitation. Compared to regular magnets, electromagnets work similarly with the exception that the attraction pull between the north and south pole is a temporary pull. As the magnets pull the vehicle upward, their current is electromagnetically regulated to maintain a constant gap between the rails and the vehicle. The magnetic field interacts with metallic loops that are conducted by conductive materials such as aluminum or copper. It supplies electric current power to the coils within the guideway to operate the direction and movement of the train along the guideway.

How Do the Motors of Maglev Trains Differ From Typical Motors?
Maglev trains do not use traditional motors, instead, the trains use linear motors. Linear motors are electric induction motors that produce a straight-line motion rather than rotational motion. The stator of the linear motors is unrolled, flat out and the "rotor" moves past it in a straight line. The position of said motors can vary from different maglev trains, so there is no definite answer. However, from most designs seen online, the motor is usually placed at the back of the train, neither at the top of the train nor in the middle of the train.

While maglev trains have been part of normal day-day-to-day life in countries such as China and Japan, there are some interesting prototypes currently in development to surpass the current speed of 430 km/h. As of three years ago, China is creating a prototype that is supposed to meet the speed rate of 600 km/h, which is in direct competition of Japan's Yamanashi maglev train that holds the winning record of 603 km/h, and has held the title of the fastest train in the world since 2015. Is it possible to even break this record? It's hard to say, but with the safety and resources given to back it up, it may be possible to see a train as fast as some of the fastest airplanes!
Written by Elina J
Works Cited:
Boslaugh, S. (2020, May 12). Maglev. Retrieved from https://www.britannica.com/technology/maglev-
train
Chandler, N. (2020, June 30). How Maglev Trains Work. Retrieved July 29, 2020, from
Wang, S., & Cripps, K. (2019, May 24). China unveils 600km/h maglev train prototype. Retrieved July
29, 2020, from https://www.cnn.com/travel/article/china-highspeed-maglev-prototype/index.html




Comments