Writing Ionic and Net Ionic Equations
- Stem To Go

- Sep 10, 2020
- 1 min read
Ionic equations are chemical equations that include spectator ions, while net ionic equations only represent the species involved in the reaction. Read on to learn how to write both of these equations!
This is the example equation we will be using:
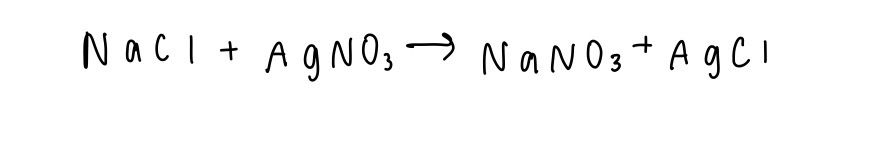
Assign states to the reactants and products. These states include aqueous (aq), liquid (l), gas (g), and solid (s). Aqueous reactants and products can be split into their individual elements, while liquids, gases, and solids can not.
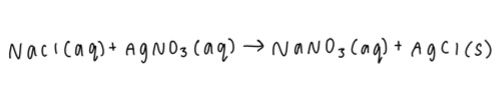
2. Split the aqueous reactants and products into individual elements and assign oxidation numbers. This is your ionic equation.
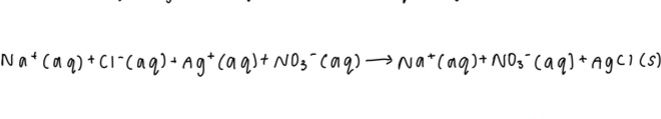
3. To write your net ionic equation, remove any elements that are seen on both ends of the equation. These are known as spectator ions- ions that do not take part in the chemical reaction and are seen before and after the reaction.
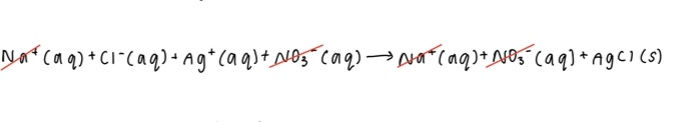
4. Rewrite your equation with the spectator ions removed; this is your completed net ionic equation.
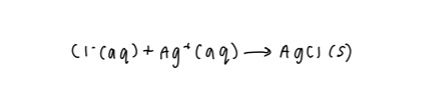
I hope this article helps you in future chemistry courses. Thanks for reading!
Written by: Ashlee Liu




Comments